Radon is a colorless, odorless gas that can pose significant health risks, particularly in residential areas. The radon map for New Jersey serves as a crucial tool for homeowners and potential buyers to assess radon levels in different regions of the state. Understanding these levels is essential for safeguarding your health and ensuring that your living environment is safe from this hazardous gas.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of radon awareness, how to interpret the radon map of New Jersey, and the steps you can take if your home is affected by high radon levels. We will also explore relevant statistics, health implications, and practical solutions for radon mitigation.
Whether you're a homeowner, real estate agent, or simply someone interested in environmental health, this guide aims to provide you with valuable insights into radon levels in New Jersey, ensuring you are well-informed and prepared.
Table of Contents
- What is Radon?
- Understanding the Radon Map of New Jersey
- Health Risks Associated with Radon Exposure
- How to Test for Radon in Your Home
- Radon Mitigation Techniques
- Radon Regulations in New Jersey
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Radon?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that is produced from the decay of uranium in the soil, rock, and water. It can seep into homes through cracks in floors, walls, and foundations, as well as through gaps around service pipes and the joints between floors and walls. Because radon is colorless and odorless, it often goes undetected unless proper testing is conducted.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States, responsible for approximately 21,000 deaths each year. Understanding radon and its risks is critical, particularly for residents of New Jersey where certain areas have been identified as having higher radon levels.
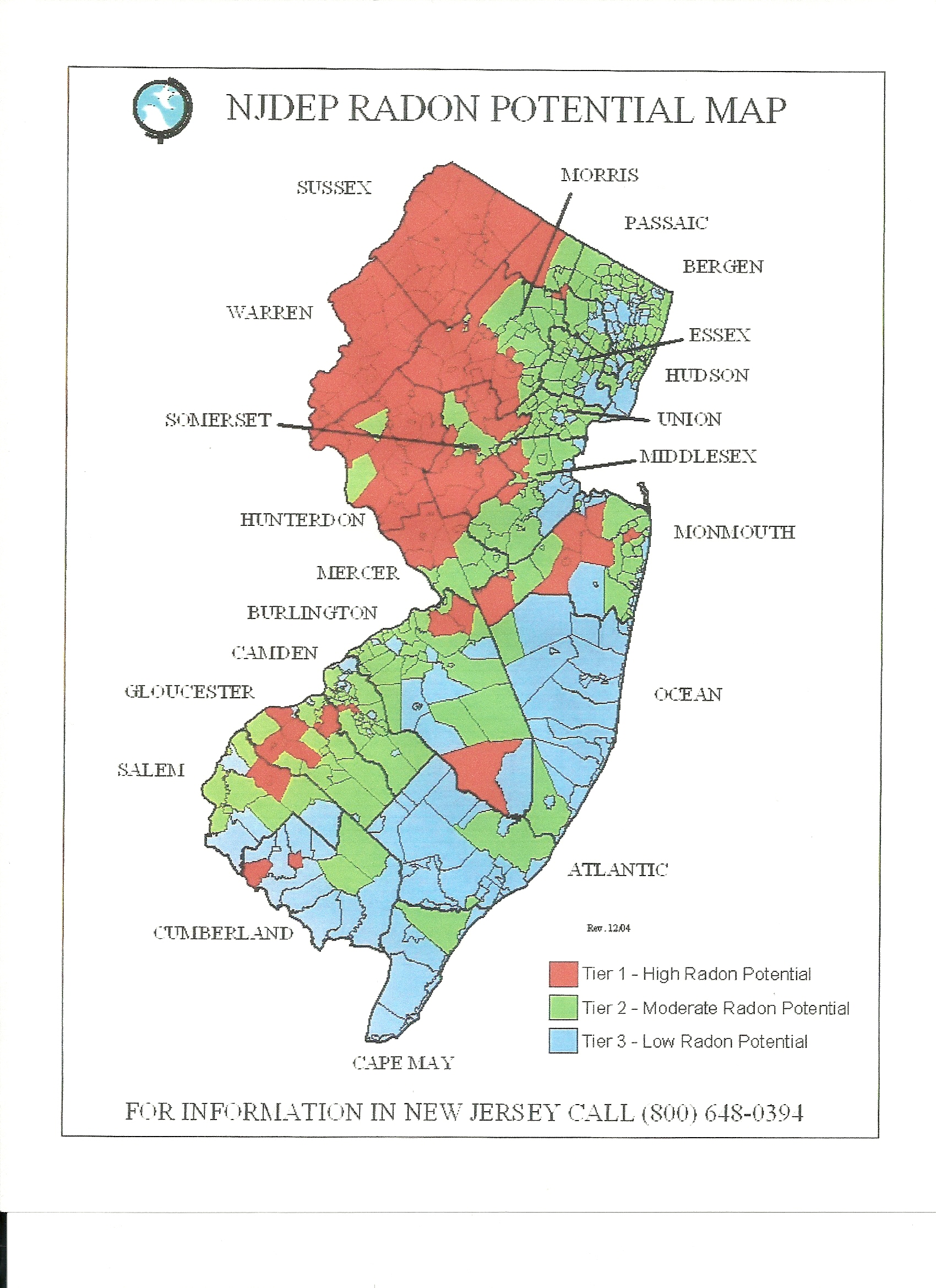
Understanding the Radon Map of New Jersey
The radon map of New Jersey provides a visual representation of radon potential across the state, highlighting areas that are more likely to have elevated radon levels. The map categorizes regions into different zones based on radon concentration levels, ranging from Zone 1 (high potential) to Zone 3 (low potential).
Categories of Radon Zones
- Zone 1: Areas with a high potential for radon exposure, with predicted average indoor radon levels greater than 4 pCi/L.
- Zone 2: Areas with moderate potential for radon exposure, with predicted average indoor radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L.
- Zone 3: Areas with low potential for radon exposure, with predicted average indoor radon levels below 2 pCi/L.
Residents in Zone 1 should take proactive measures to test their homes for radon and consider mitigation strategies if levels are found to be elevated. Meanwhile, those in Zones 2 and 3 should still remain vigilant, as radon can be present in any home regardless of the mapped zone.
Health Risks Associated with Radon Exposure
Exposure to high levels of radon gas can lead to serious health issues, primarily lung cancer. The risk increases with the amount of radon inhaled and the duration of exposure. The EPA estimates that radon is responsible for about 21,000 lung cancer deaths annually, making it a significant public health concern.
Symptoms of Radon Exposure
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Frequent respiratory infections
It's important to note that radon exposure does not typically produce immediate symptoms, making testing crucial for detecting harmful levels.
How to Test for Radon in Your Home
Testing for radon is the only way to know if your home has elevated levels of this gas. Fortunately, the process is straightforward and can be done using radon test kits available at hardware stores or online.
Types of Radon Test Kits
- Short-term Test Kits: These kits measure radon levels for a period of 2 to 90 days, providing quick results.
- Long-term Test Kits: These kits measure radon levels for more than 90 days, giving a more accurate picture of average radon concentrations.
After conducting a test, if radon levels are found to be 4 pCi/L or higher, it is recommended to take action to mitigate the levels.
Radon Mitigation Techniques
If your home has elevated radon levels, several mitigation techniques can be implemented to reduce radon concentrations effectively. Some common methods include:
Common Radon Mitigation Methods
- Sub-slab Depressurization: This involves installing a vent pipe system and fan to pull radon from beneath the house and vent it outside.
- Block Wall Depressurization: This method is used for homes with hollow block walls, where suction is applied to the block walls to reduce radon entry.
- Drain Tile Depressurization: Similar to sub-slab depressurization, but specifically for homes with drain tile systems.
- Sealing Cracks and Openings: While this method is less effective on its own, sealing cracks and openings can help reduce radon entry.
It's essential to hire a qualified radon mitigation contractor to ensure the selected method is properly installed and effective.
Radon Regulations in New Jersey
New Jersey has specific regulations in place regarding radon testing and mitigation. The New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP) recommends that all homes be tested for radon, especially during real estate transactions.
Furthermore, the state mandates that real estate professionals inform buyers about radon testing and provide them with the opportunity to conduct radon tests before finalizing a sale. These regulations aim to protect public health and increase awareness about the risks associated with radon exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions regarding radon and its impact:
What should I do if my home has high radon levels?
If your home tests above 4 pCi/L, it is important to take action immediately. Consider hiring a certified radon mitigation contractor to discuss the best mitigation options for your home.
Can radon levels change over time?
Yes, radon levels can fluctuate due to various factors, including weather conditions and changes in the home’s structure. Regular testing is recommended to ensure levels remain safe.
Conclusion
Understanding the radon map of New Jersey and the associated health risks is vital for ensuring the safety of your home and family. By testing for radon and taking appropriate mitigation measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of radon exposure.
We encourage you to take action today—test your home for radon, educate yourself about mitigation techniques, and share this information with friends and family. Together, we can create a safer living environment for everyone.
If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences, please leave a comment below. Don't forget to explore our other articles for more information on health and environmental safety!
- Carol Luistro Obituary
- Did Kamala Harris Used To Date Montel Williams
- Brandon Steven Net Worth Forbes
- Molly Roloff Kids
- Sophie Rain Naked
- Desirulezco
- Heather Robinson Tim Robinson
- Yololary Onlyfans
- Porn Camilla Araujo
- Sophie Rain Spiderman Erome

![Untitled Document [www.state.nj.us]](https://i2.wp.com/www.state.nj.us/dep/rpp/radon/images/radon2004letter.jpg)